Leaning process
In the process of learning using LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation), we start by creating a Base model and conducting fine-tuning to generate LoRA, which enhances the model’s flexibility towards new data. Subsequently, we combine LoRA with the base model to create a new model capable of continuous learning.
After incorporating LoRA into the primary model, the results can be used to merge with other models or applied directly. This enables the model to exhibit continuous learning abilities and adapt well to new data.
Ultimately, adopting the LoRA approach proves to be an effective method in imparting the model with adaptability for continuous learning and seamless integration with other models in research endeavors.
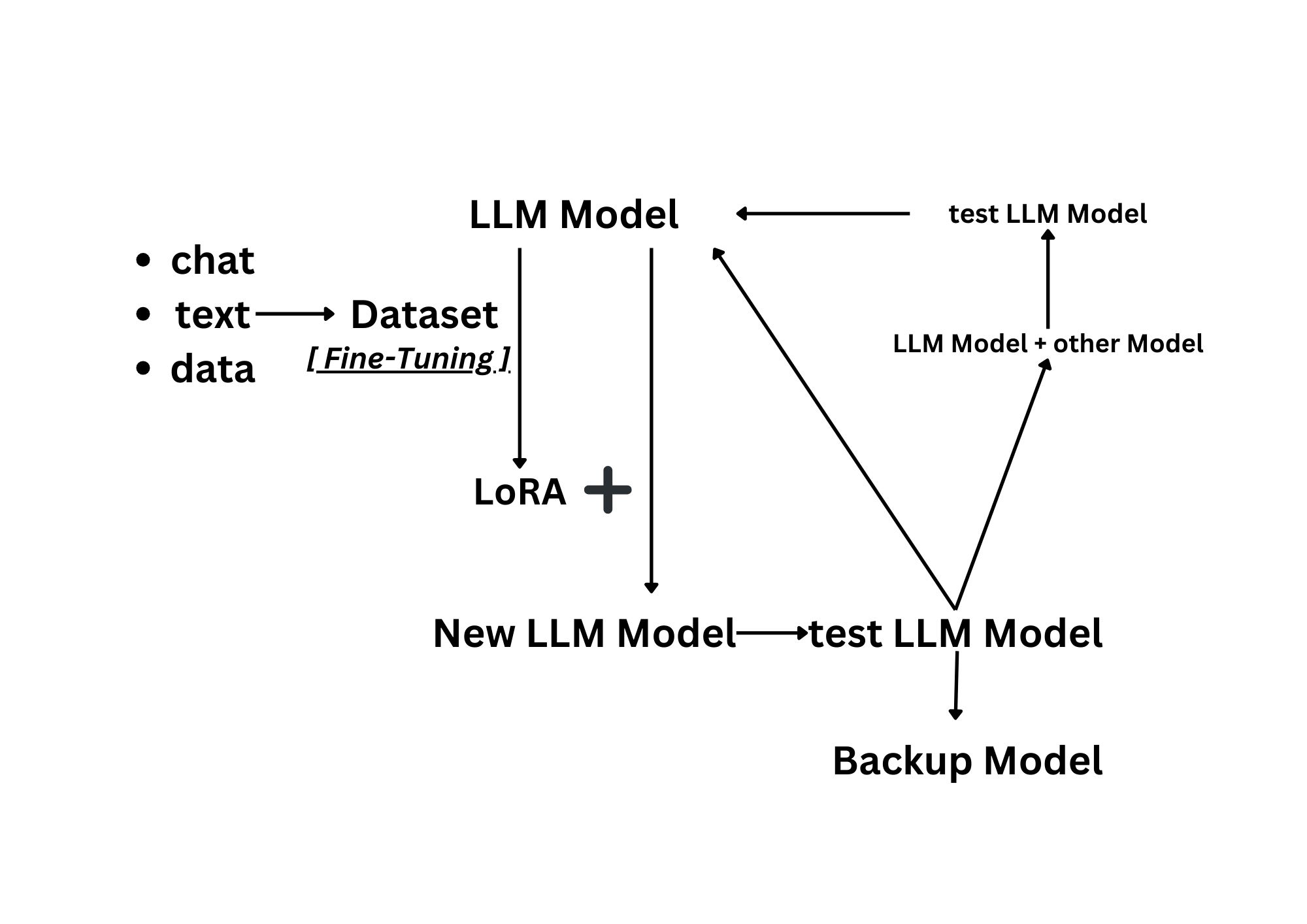
The diagram illustrates the operational principles of model learning, showcasing its ability to gather information through diverse channels such as alternative data sources, user interactions, and independent data retrieval. This results in a significant diversity among individual models, each capable of learning from distinct sources, contributing to a rich and varied spectrum of knowledge. This variance in learning approaches can have profound implications for future research endeavors, emphasizing the concept of iterative and reinforced thinking processes.
In summary, the depiction highlights the model’s capacity to assimilate information from various avenues, fostering a broad range of learning experiences. This diversity in learning methods among individual models can be instrumental in shaping innovative research strategies and underscores the essence of repetitive and reinforced cognitive processes.